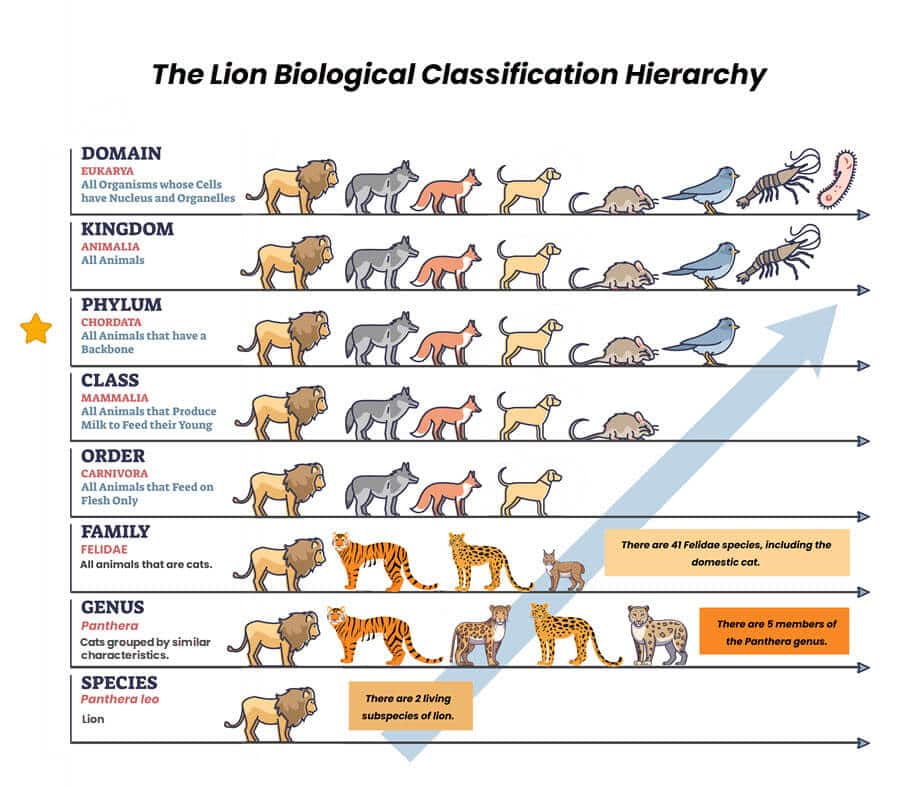
Phylum
Phylum is the classification below kingdom and above class. The term “division” is used for plants.
Organisms are classified in a phylum (or division) mostly based on their body structure. Animals of the phylum Chordata have an internal skeleton and a backbone or notochord (a primitive backbone). This group includes fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. There are approximately 31 different types of phyla.
Wild cats are part of the phylum Chordata.
More about Phylum
A phylum is a way scientists group living things that are similar to each other. It’s like putting animals or plants into big categories based on how their bodies are built or how they work. For example, all animals with backbones, like humans, dogs, wild cats and birds, are in one phylum called Chordata. Another phylum, Arthropoda, includes creatures with hard outer shells and jointed legs, like insects, spiders, and crabs.
The word phylum comes from an old Greek word, phylon, which means “tribe” or “group.” Scientists started using it in the 1800s to help organize the millions of different living things on Earth. A German scientist named Ernst Haeckel helped make the term popular in biology around 1866. He used it to describe big groups of animals that share key traits, like how their bodies are shaped or how they grow.