North American wild cats include two big cats, the jaguar and cougar, and smaller wild cats like the ocelot, jaguarundi, bobcat and Canada lynx.
North America is the third-largest continent on the planet. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean (south), Atlantic Ocean (east), Arctic Ocean (north), South America, and the Caribbean Sea (southeast).
More About North America
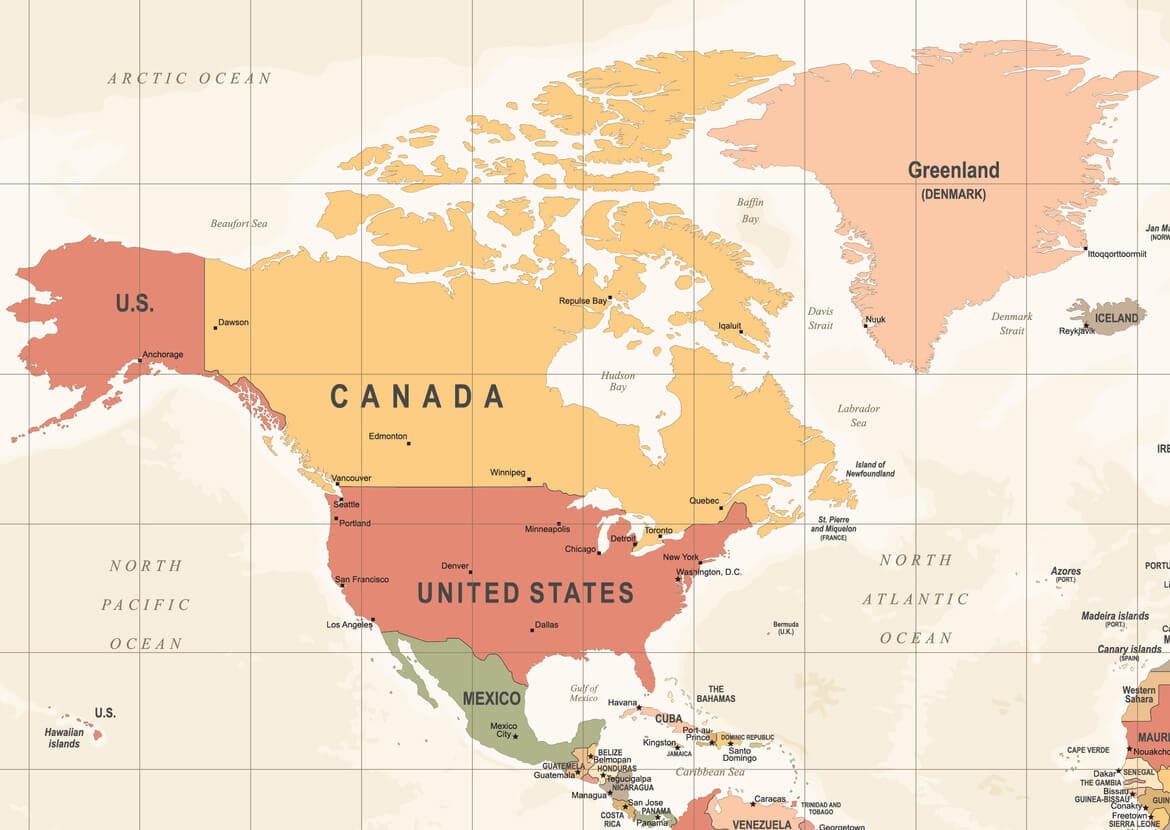
North America is home to three major countries: Canada, the United States, and Mexico. In addition to these, the continent also includes Central America and the Caribbean. The geography of North America is incredibly varied, ranging from snow-covered mountains and large forests to deserts and tropical rainforests.
Countries of North America
North America consists of three large countries—Canada, the United States, and Mexico—as well as the smaller nations of Central America and the Caribbean. These countries are all part of the same continent, yet each has its own unique culture, history, and landscape.
Canada is the northernmost country in North America. Known for its cold winters, beautiful forests, and many lakes, it is the second-largest country in the world by land area. Its population is mostly concentrated near the southern border with the United States.
The United States is located just south of Canada and is made up of 50 states. The country has a wide variety of climates and landscapes, from the beaches of Florida to the mountains of Colorado and the deserts of Arizona. The U.S. is also home to many major cities and cultural landmarks.
Mexico is located south of the United States and is the third-largest country in North America. Mexico is known for its rich history, including ancient civilizations like the Aztecs and Mayans. It has diverse geography, from the deserts in the north to tropical rainforests in the south.
The Geography of North America
The North American continent includes many different types of landforms and climates.
Northern Canada is mostly cold and covered in forests and tundra. It has long winters and short summers. There are also large mountain ranges, like the Rocky Mountains, which run through both Canada and the United States. The Canadian Shield, a large area of ancient rock, covers much of eastern and northern Canada.
The United States has a mix of different landscapes. In the west, you’ll find the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada mountain ranges. The Great Plains stretch across the middle of the country, while the Appalachian Mountains are in the east. The U.S. also has coastal areas along the Atlantic Ocean in the east and the Pacific Ocean in the west. Deserts, like the Mojave Desert and the Sonoran Desert, are found in the southwest, while forests and lakes are common in the Northeast and Great Lakes regions.
Mexico is home to a wide range of environments. The northern part of the country is dry and desert-like, while the southern regions are lush and tropical. The Sierra Madre mountain ranges run through the country, and the Yucatán Peninsula is known for its beautiful beaches and ancient Mayan ruins.
Central America: Bridging North and South America
One of the most interesting parts of North America is Central America. This region, which includes countries like Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama, is located between Mexico in the north and Colombia in the south. Central America is sometimes seen as its own region, but it is also considered part of the North American continent.
Central America serves as a land bridge between North and South America. This is a narrow strip of land that connects the two continents, making it an important geographical feature. The region is home to many unique ecosystems, including rainforests, volcanic mountains, and coastlines along both the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
The countries of Central America have distinct cultures and languages, but they all share similarities in their geography. The region is prone to tropical storms and hurricanes, especially during the rainy season. It also has a mix of mountainous areas, coastal plains, and tropical rainforests.
North American Wild Cat Species
North America is home to several different species of wild cats:
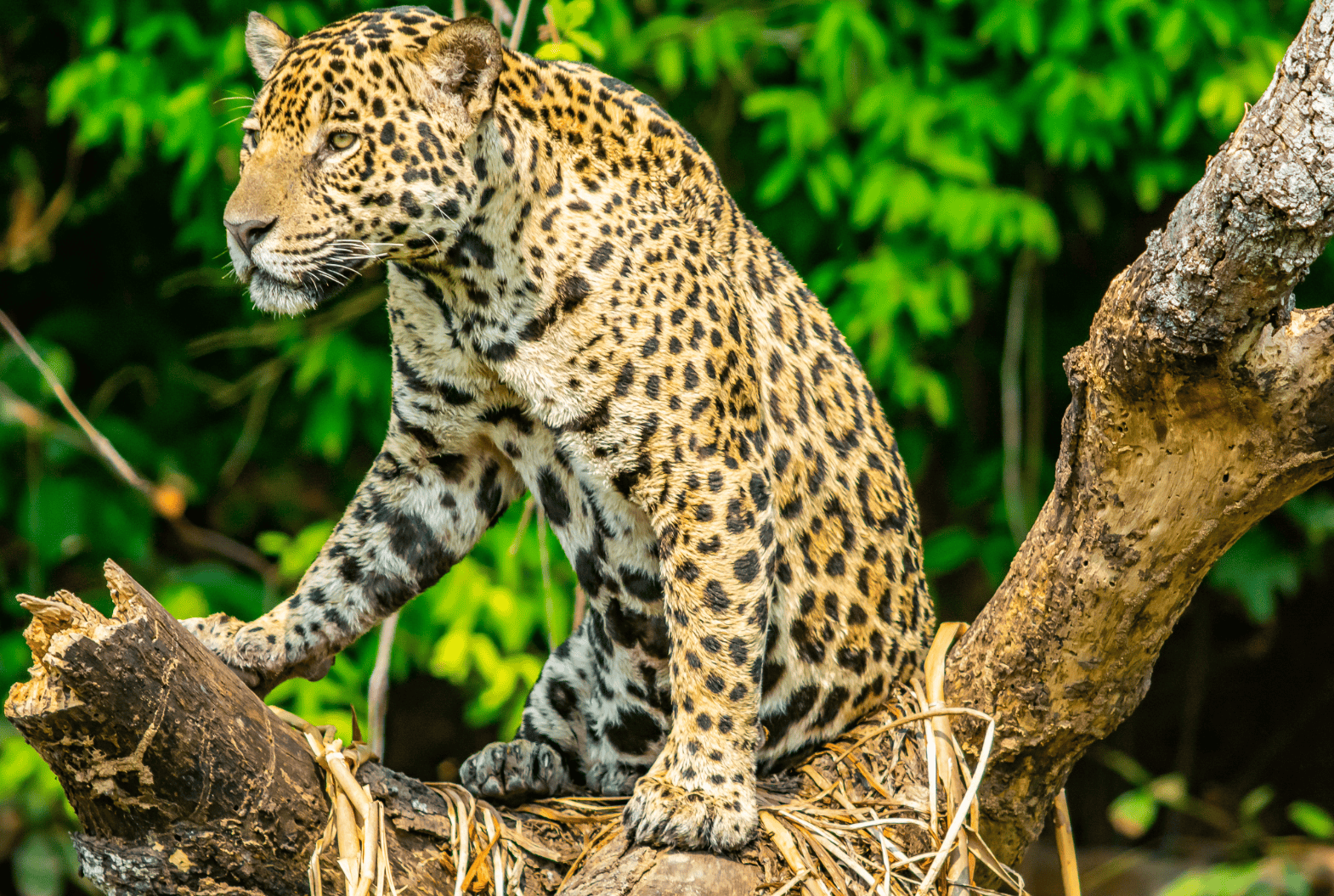
- Jaguar (Panthera onca) – The biggest wild cat in North America.

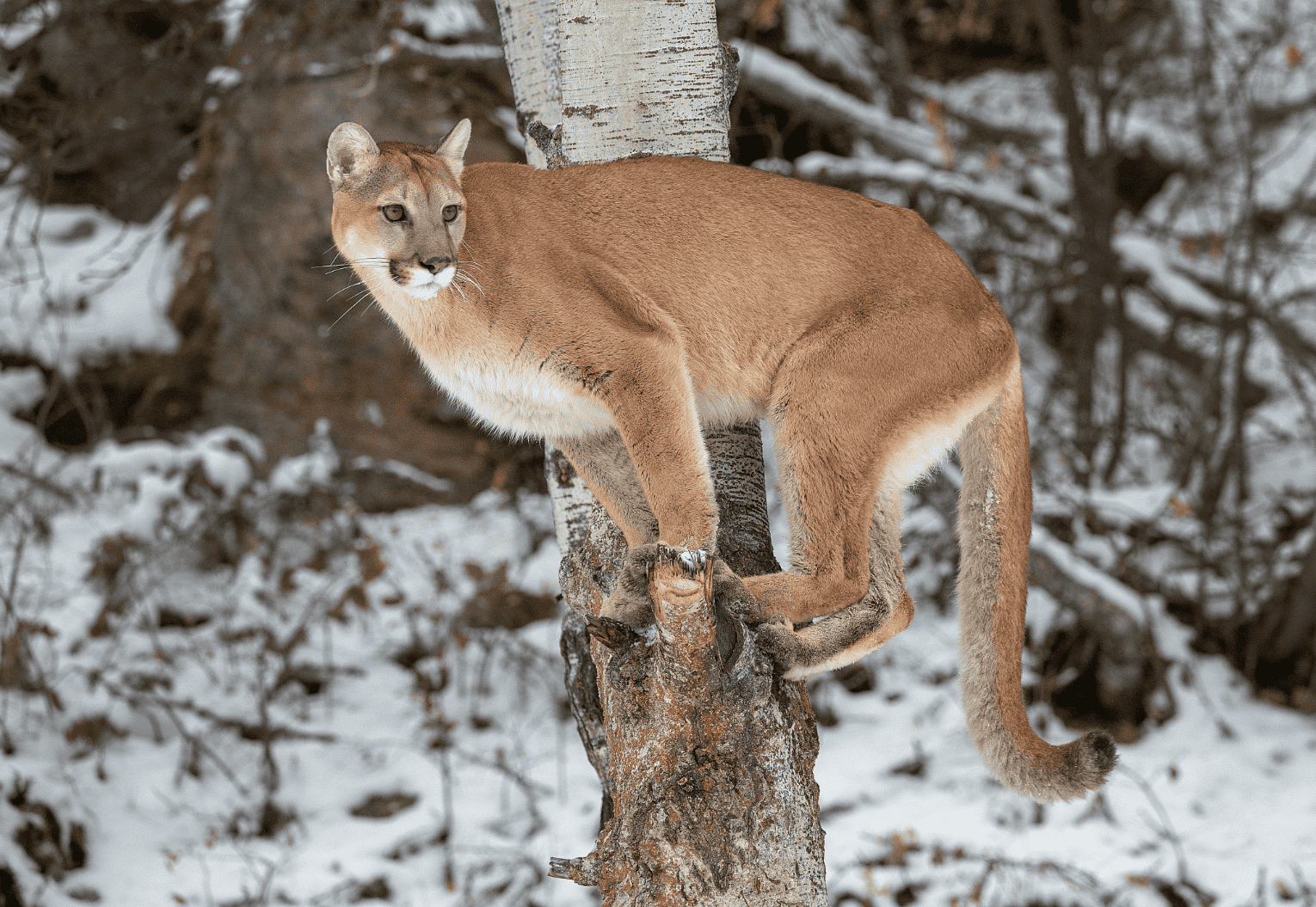
- Cougar (Puma concolor) – North America’s second-biggest wild cat. It can be found from Canada down to South America.

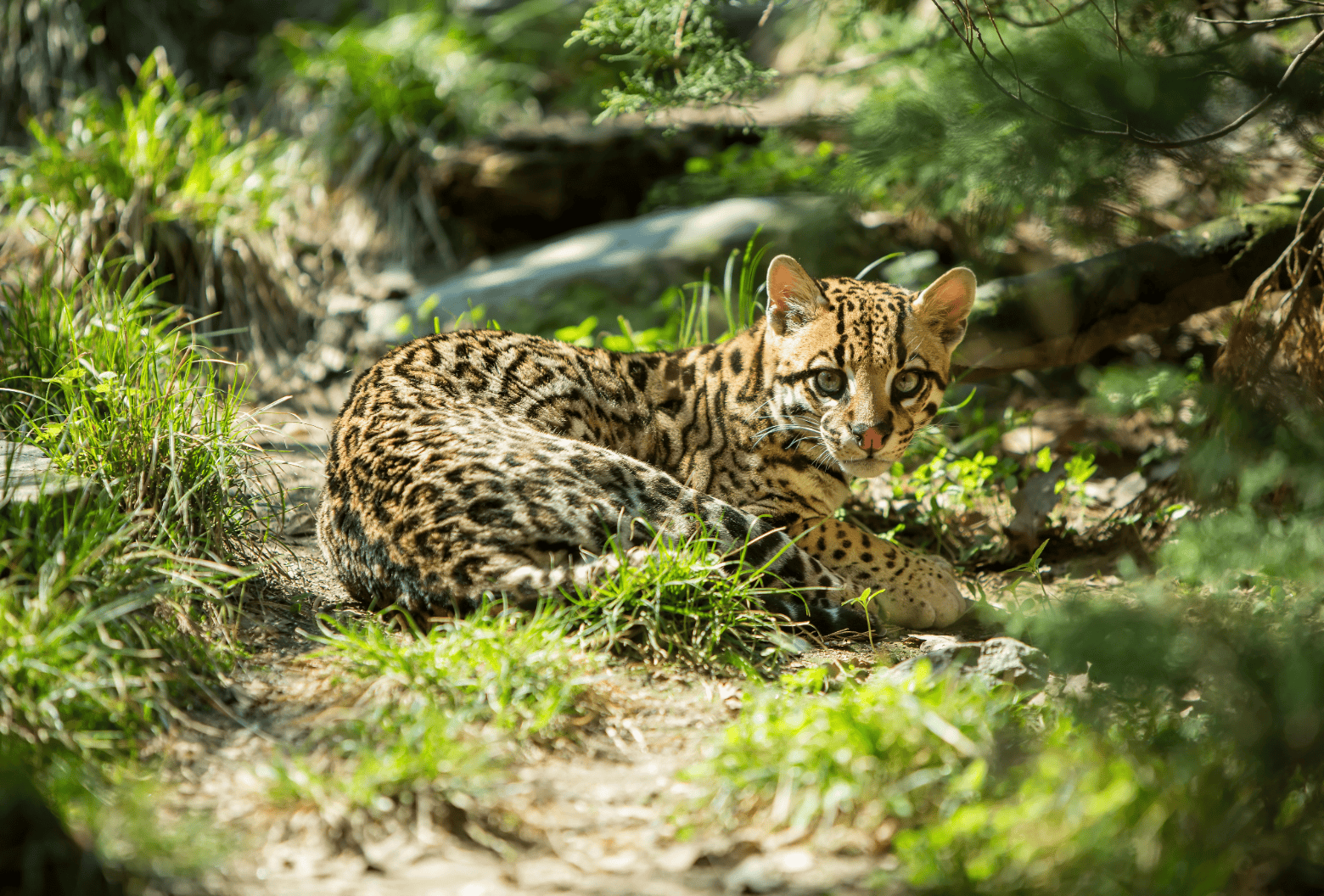
- Ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) – Twice as big as a household cat.

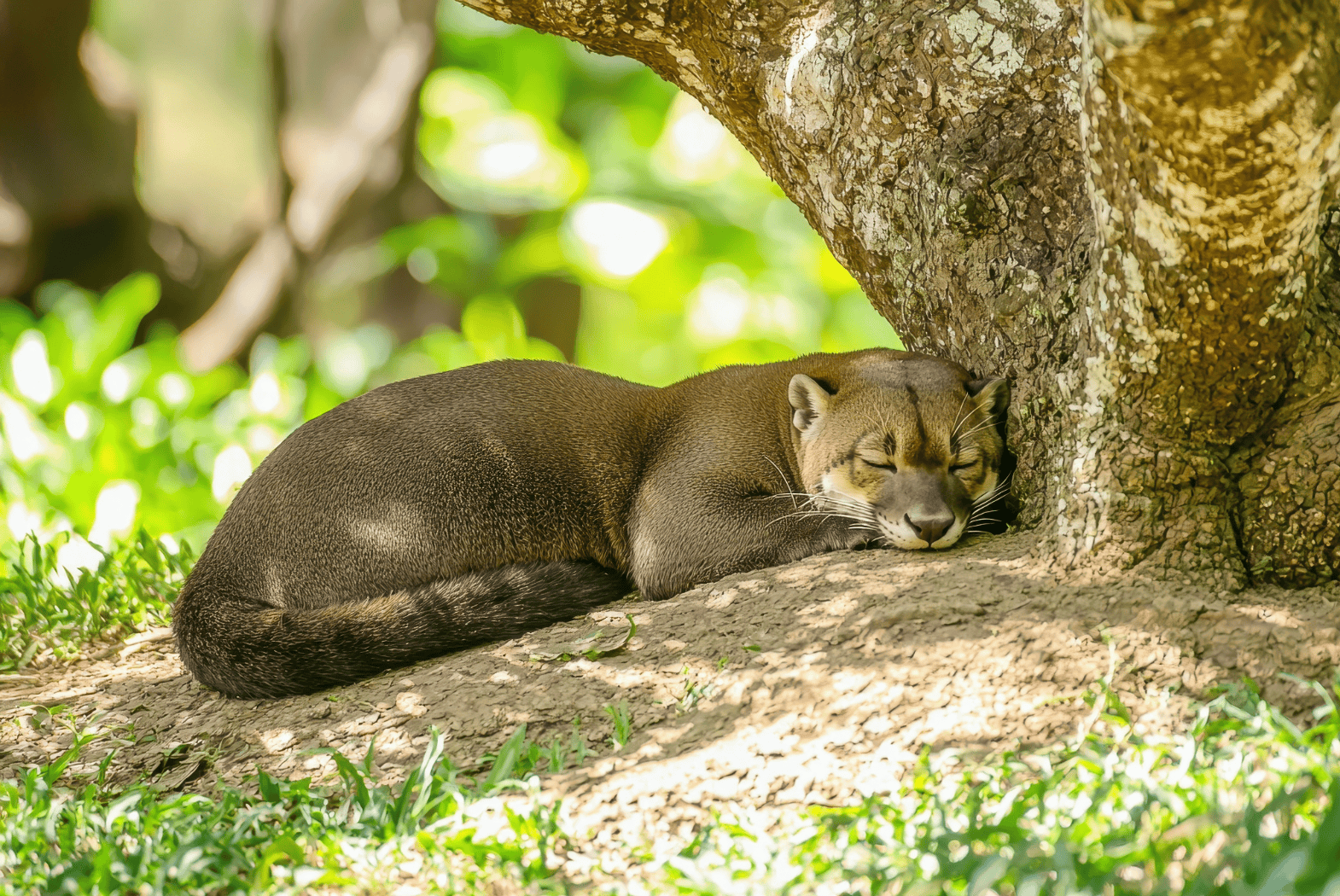
- Jaguarundi (Herpailurus yagouaroundi) – A medium-sized wild cat with a very long body.

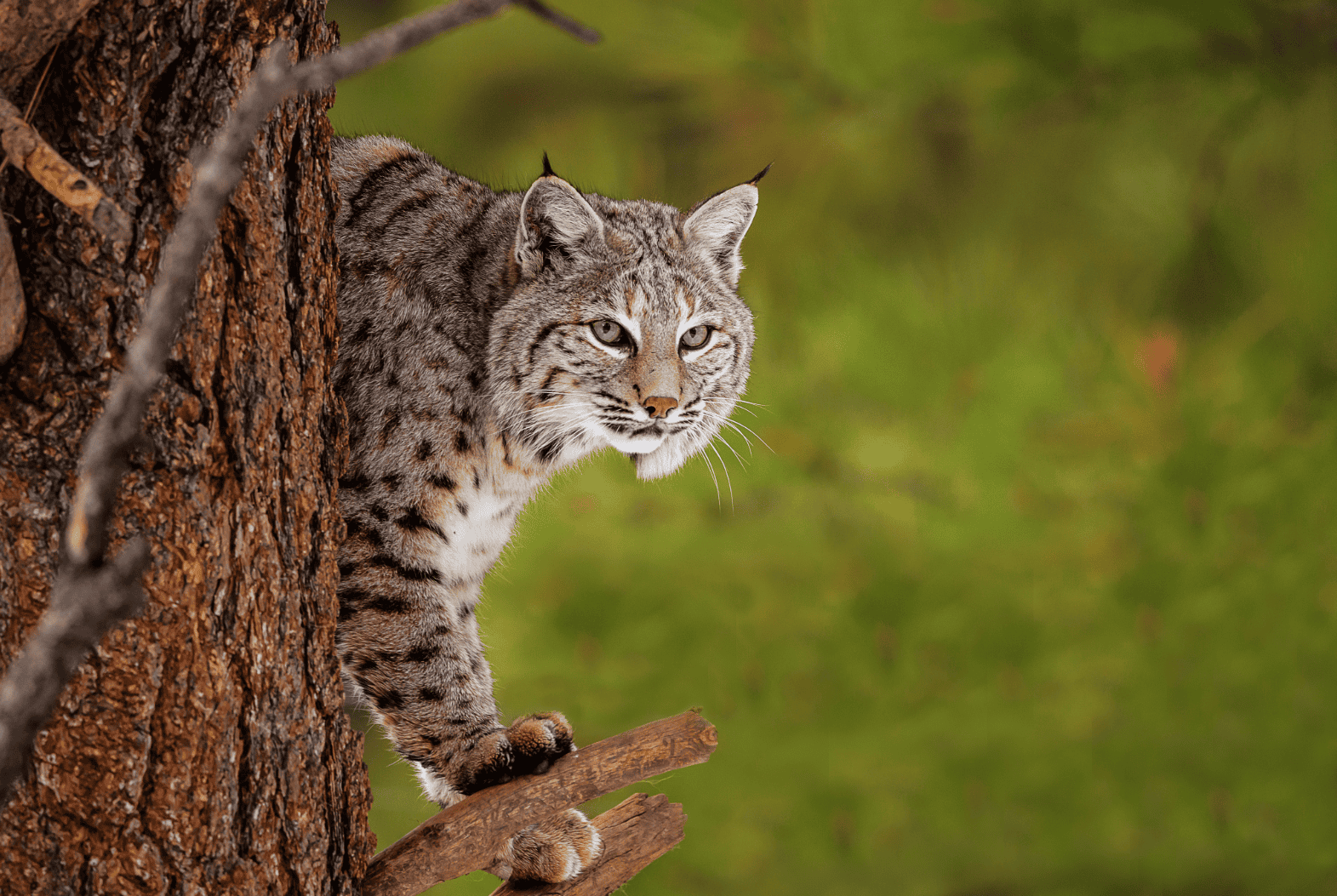
- Bobcat (Lynx rufus) – Has a similar appearance to a Canadian lynx.

- Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis) – A medium-sized wild cat with thick fur, long legs, big paws, a black-tipped tail, and ear tufts.
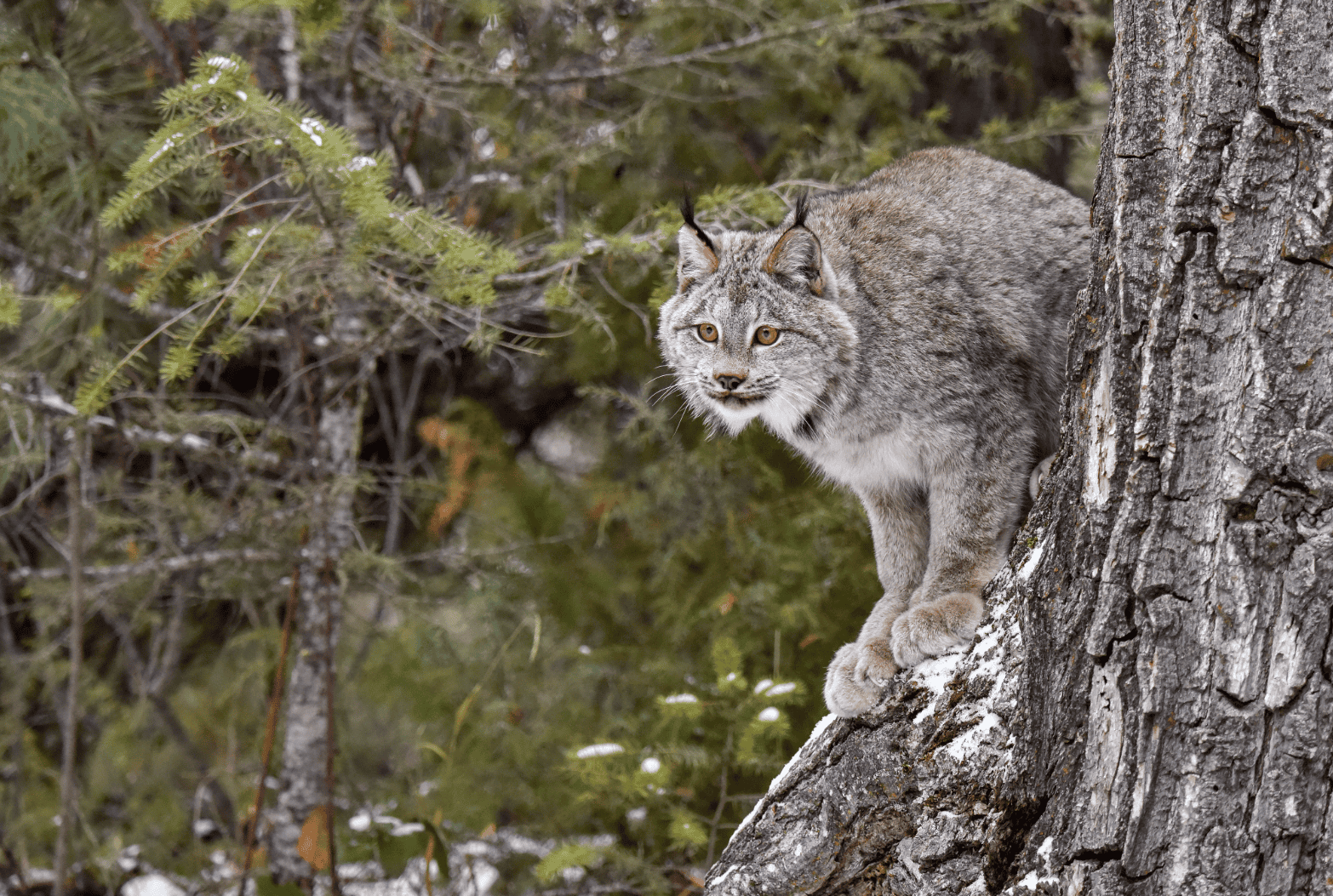
North American Wild Cat Habitat
From the cold, snowy landscapes of Canada to the warm tropical jungles of Central America, wild cats can be found in a variety of North American habitats.
The jaguar is primarily found in the southern parts of the continent. While historically, jaguars roamed large areas of the southern United States, their range has shrunk over the years. Today, jaguars are most commonly found in the tropical forests of Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America. In the U.S., jaguars are extremely rare, with a few individuals occasionally spotted in southern Arizona and Texas, where efforts are underway to protect them and expand their range. Jaguars prefer dense rainforests, riversides, and wetlands, where they can hunt for a wide range of prey, such as deer, capybaras, and even caimans. They are powerful swimmers and are often found near water.
The cougar, also known as the mountain lion or puma, has the largest range of any wild cat in North America. These cats are found throughout much of Canada, the United States, and Mexico. In Canada, they are most common in British Columbia and the Rocky Mountains. In the U.S., mountain lions range from the western states like California and Colorado to parts of the Midwest and even the eastern regions of the country, including Florida. Mountain lions are adaptable cats, capable of surviving in a wide range of habitats, including forests, mountains, deserts, and even suburban areas. They are solitary and prefer rugged, remote landscapes where they can hunt prey such as deer and elk.
The ocelot is a small wild cat that inhabits parts of Mexico, Central America, and the southern United States. Ocelots are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical forests, but they also live in savannas and dry forests. In the U.S., their range is limited to southern Texas and Arizona, where they are considered rare and endangered. Ocelots are nocturnal hunters, preying on smaller animals like rodents, birds, and reptiles. Their beautiful spotted coats help them blend into their forest environments, making them skilled ambush predators.
The jaguarundi is another small wild cat that inhabits Mexico and Central America, as well as parts of South America. Unlike the ocelot, jaguarundis are more often found in open savannas, grasslands, and semi-arid regions. In the U.S., jaguarundis have been spotted in south Texas but are extremely rare. These cats are less dependent on dense forest cover compared to other wild cats, making them well-suited to open landscapes. Jaguarundis are primarily carnivorous, hunting small mammals, birds, and reptiles. They are known for their distinctive, elongated bodies and short, sleek coats.
The bobcat is one of the most widespread wild cats in North America. They are found throughout Canada, the United States, and parts of Mexico. Bobcats are highly adaptable and can live in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, grasslands, and even suburban areas. In the U.S., they are common in almost every state, except for those in the extreme northeast and some parts of the Midwest. Bobcats are solitary hunters, preying on a variety of animals such as rabbits, squirrels, and birds. They are skilled at stalking and ambushing prey, often hiding in brush or trees before pouncing.
The Canada lynx is found in Canada and parts of the northern United States, particularly in Alaska, the Rocky Mountains, and the Great Lakes region. Canada lynx are adapted to cold environments, with thick fur and large paws that act as natural snowshoes. They primarily inhabit dense forests and woodlands, often in remote areas far from human activity. Canada lynx are known for hunting snowshoe hares, which make up the bulk of their diet. They are expert climbers and can move silently through the snow, making them efficient predators in their snowy habitats.
Conservation Issues
Wild cats in North America, including those found in Canada, the United States, and Central America, face a variety of conservation challenges. Many of these cats are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
One of the biggest threats to wild cats in North America is habitat loss. As human populations grow, forests, grasslands, and other natural habitats are cleared for farming, urban development, and infrastructure. This leaves wild cats with smaller, fragmented areas in which to live. The loss of habitat makes it harder for wild cats to find food, shelter, and mates.
For example, the jaguar, once found throughout much of the southern United States, now has a much smaller range in the U.S., mainly in southern Arizona and Texas. As these areas are developed for agriculture and human settlements, jaguars lose the forests and wetlands they depend on. This also increases the likelihood of human-wildlife conflicts, as cats wander into populated areas looking for food.
Poaching and Illegal Trade
Poaching is another significant issue for wild cats in North America. Some wild cats, like the jaguar and the ocelot, are targeted for their beautiful fur, which is sold illegally on the black market. These animals are also hunted for their bones and other body parts, which are used in traditional medicine or as trophies.
For example, the ocelot has been heavily poached in Central America for its striking coat pattern. The illegal fur trade has pushed the population of ocelots to dangerous levels in some areas. Many countries in Central America have started to enforce stricter laws against poaching, but enforcement can be difficult in remote areas where illegal activity is hard to track.
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), “Poaching for skins and body parts remains a major threat for many species of wild cats in North America, particularly the jaguar and ocelot”.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
As human populations expand, wild cats are increasingly coming into conflict with people. This is particularly true in areas where bobcats or mountain lions live near suburban developments. When these cats roam into human settlements in search of food, they may be seen as a threat to livestock or pets. This often leads to attempts to capture or kill the animals.
In California, for example, mountain lions have been known to enter suburban neighborhoods. While most of these animals simply pass through, some are trapped and relocated, or even killed, due to fear of attacks on humans or pets.
Conservation Efforts and Solutions
Despite the challenges, there have been many efforts to protect wild cats across North America. In some areas, wildlife corridors are being created to help animals move safely between fragmented habitats. These corridors are important for species like the cougar, which needs large territories to survive.
In addition, laws protecting wild cats are becoming stricter. The Endangered Species Act in the U.S. has helped protect the jaguar and Canada lynx in some areas. Local and national organizations are also working to raise awareness about the importance of wild cats and their role in ecosystems.
Article Resources
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), https://www.iucn.org
- International Union for Conservation of Nature/Cats Specialist Group, https://www.catsg.org/













0 Comments