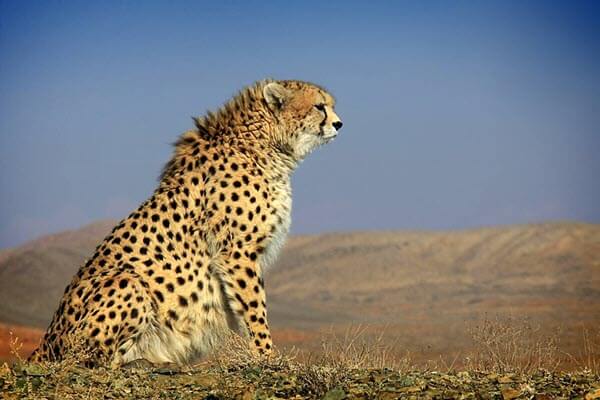
The Asiatic cheetah is a subspecies of cheetah that can be found in the deserts of Iran. The cat is also called the Persian cheetah and Iranian cheetah.
The Asiatic cheetah once lived in India, Afghanistan, Arabia and Pakistan. Now there are only small groups of Asiatic cheetahs in various Iranian reserves, with occasional sightings in Pakistan. It is estimated that there are less than 100 cats currently living in the wild.
Scientific Name: Acinonyx jubalus venaticus
Conservation Status: Critically Endangered (as of January 2022, only 12 cheetahs remain in existence).
Subspecies: None
Meaning of the name
“Asiatic” means coming from Asia. The word “cheetah” is from the Sanskrit word citrakayah (“citra” meaning displaying different spots streaks, and “kaya” meaning body).
Som Asiatic cheetah facts
- Can only be found in the deserts of Iran.
- Has a smaller head than African cheetahs.
- Has shorter legs than an African cheetah.
- Has a stronger neck than an African cheetah.
History
The Asiatic cheetah is generally believed to have separated from African cheetahs somewhere between 32,000 and 67,000 years ago.
More recent research places the separation at 5,000 years ago. At one time, cheetahs were tamed and trained to hunt.
What Asiatic cheetahs look like
 The Asiatic cheetah can grow (from head to body) up to 4.5 feet long, with a tail almost 3.5 feet in length. Their heads are smaller than African cheetahs. The cat’s fur is tan with black spots. They also have a stripe that runs from the corner of the eyes to the nose and mouth area.
The Asiatic cheetah can grow (from head to body) up to 4.5 feet long, with a tail almost 3.5 feet in length. Their heads are smaller than African cheetahs. The cat’s fur is tan with black spots. They also have a stripe that runs from the corner of the eyes to the nose and mouth area.
Asiatic cheetah habitat
Asiatic cheetahs prefer open habitats, such as plains and deserts. Most of the remaining cats can be found in five national parks and sanctuaries:
- Touran National Park
- Daranjir Wildlife Reserve
- Naybandan Wildlife Reserve
- Kavir National Park
- Bafq Protected Area
Cheetah males will establish a territory. Females will frequently travel, sometimes for very long distances.
Hunting and food
The Asiatic cheetah primarily preys on gazelle, but will also eat wild goats, sheep and hare.
Reproduction
 Cheetah males will seek out female cheetahs for mating at approximately one year of age. The females begin to mate at two years of age. Cheetah males have a low sperm count, resulting in a low number of cheetah births.
Cheetah males will seek out female cheetahs for mating at approximately one year of age. The females begin to mate at two years of age. Cheetah males have a low sperm count, resulting in a low number of cheetah births.
The female cheetah gestation period is 90 to 100 days. Female cheetahs can have up to 9 cubs, but most will end up dying due to predators.
The female cheetah will take care of her cubs and travel with them until they reach 1 to 1.5 years of age. After the cheetah mother leaves, the young females will go off on their own. The males will stay together or, in the case of only one or two males, join another group of males.
Asiatic Cheetah Conservation Issues
Asiatic cheetahs prey on wild goats, sheep and gazelle. Although cheetahs are known to inhabit desert areas and plain, some Iranian cheetahs can be found in more rugged, mountain-like terrain.
The Asiatic cheetah’s near extinction is the result of hunting, loss of prey, human conflict and loss of habitat.
Asiatic cheetah conservation organizations…


intresting to now know and love,love,love cheetah’s
the pic was to cute.
Hi, yes, you can. Please mention where you got the information from – bigcatswildcats.com
can i borrow this info for a school progect
I’m using this for a school project.